+919360391740
gastrosurgeondrkumar@gmail.com
Appendicitis
- Home
- Appendicitis
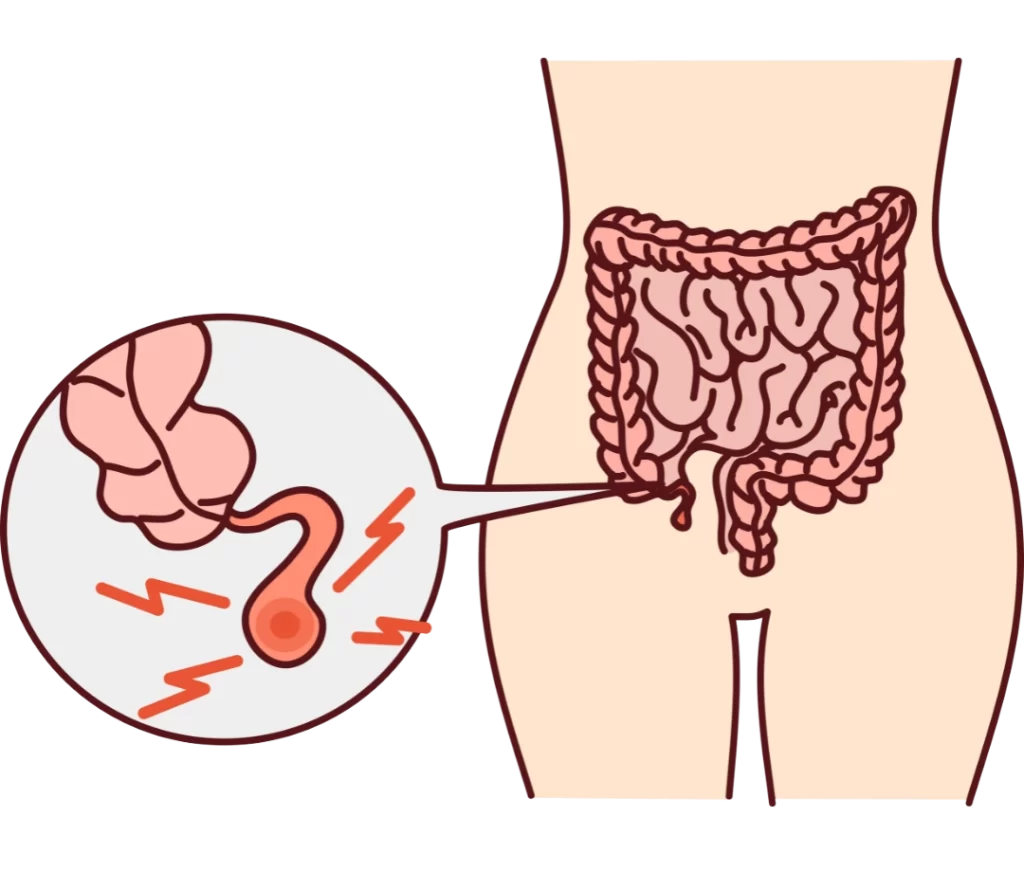
APPENDIX – The appendix is a muscular and tubular organ that is joined to the large intestine near its junction with the small intestine and it is usually present in the right lower abdomen. The appendix protrudes from the cecum a pouch-like structure in the large intestine at its lower end near its junction with the small intestine. The appendix typically has a diameter of 7 to 8mm and a length of 2 to 20 cm with an average length of 9cm.
APPENDICITIS – Appendicitis is infection of the appendix and is a painful condition in which the appendix becomes inflamed and filled with pus, a fluid made up of dead cells and inflammatory tissue that often results from an infection. The appendix becomes large and enlarged and the infection may spread to the surrounding tissues and the appendix may become rotten and several times it may burst causing peritonitis.
Causes Of Appendicitis
A blockage in the lining of the appendix that results in infection is the likely cause of appendicitis. The bacteria multiply rapidly, causing the appendix to become inflamed swollen, and filled with pus.If not treated promptly the appendix can rupture. Constipation can lead to an appendicolith in the appendix, which can lead to appendicitis. Intestinal infection can spread to the appendix leading to appendicitis.
Symptoms Of Appendicitis
Sudden pain that begins on the right side of the lower abdomen, Sudden pain that begins around the navel and often shifts to the lower right abdomen, Pain that worsens while coughing, walking or making other jarring movements, Nausea and vomiting, Loss of appetite, Low-grade fever that may worsen as the illness progresses, Constipation or diarrhea, Abdominal bloating, Flatulence
The site of pain may vary, depending on the patient’s age and position of the appendix and the severity of appendicitis, but most of the time the pain is in the right lower abdomen.
Complication Of Appendicitis
Peritonitis, Rupture,Perforation, Gangrenous, Abscesses, Sepsis
PERITONITIS – If the appendix bursts, the lining of the abdomen (peritoneum) will become infected with bacteria. This is called peritonitis. Internal organs can also be damaged.
APPENDICULAR ABSCESSES – Abscess forms around a burst appendix. This is a painful collection of pus that forms when the body tries to fight the infection and the appendix is surrounded by pus and it is an emergency situation that needs to be operated on urgently.
APPENDICULAR MASS – Sometimes the surrounding intestines adhere to the appendix forming a mass. This is a late presentation of improperly treated appendicitis and many times may have to be conservatively treated with medicines and planned for interval appendicectomy later.Most of the time the appendicular mass can be diagnosed on CT scan.
Diagnosis
Most of the time the doctors examining the patient may clinically diagnose appendicitis however the diagnosis of appendicitis can be confirmed by doing a CT scan of the abdomen/ultrasound of the abdomen /biochemical blood investigations.
Treatment Of Appendicitis
Treatment usually involves surgery to remove the inflamed appendix.Before surgery, a dose of antibiotics given to treat infection.
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY – Laparoscopic surgery (keyhole surgery)entails making 3 small keyholes in the abdomen and inserting a miniaturized camera and laparoscopic surgical instruments. The surgeon then removes the appendix with the laparoscopic instruments, eliminating the need for a big incision in the belly. Most of the time laparoscopic surgery is done to remove the appendix.
Dr.KUMARAGURUBARAN has a huge experience and he is an expert in laparoscopic appendicectomy procedure.
OPEN APPENDECTOMY – Even though most of the time laparoscopic is done to remove the appendix very rarely sometimes open surgery may be required to remove the appendix. Open surgery is recommended when the appendix has already burst and formed a lump and a complicated situation arises when there is widespread infection of the inner lining of the abdomen.
Most of the time DR.KUMARAGURUBARAN removes the appendix by laparoscopic even in the most complicated cases and only in rare cases open surgery is performed.
Types Of Appendicitis
SUBACUTE APPENDICITIS – Many times the infection with the appendix is mild and the symptoms may not be severe it is called subacute appendicitis.
ACUTE APPENDICITIS – When the infection and the pain is suddenly onset it is acute appendicitis.
RECURRENT APPENDICITIS – Sometimes the appendicular infection comes mildly and then disappears and becomes alright and then pain recurs later. This is called Recurrent appendicitis.
PERFORATED APPENDIX – It is one of the complications of acute appendicitis.When appendicitis is left untreated, necrosis of the appendiceal the wall can occur and progress to a focal rupture.
GANGRENOUS APPENDICITIS – Pain in the appendix with necrosis of the wall of the appendix and most commonly developing in obstructive appendicitis. And the appendix becomes gangrenous.
APPENDICULAR MASS – sometimes the appendix becomes infected and forms a mass with the surrounding intestine, which is called appendicular mass.
APPENDICULAR ABSCESS – sometimes the appendix gets infected leading to pus formation and forming appendicular abscess.
APPENDICOLITH – A calcified deposit found inside the appendix is called an appendicolith. They can be an incidental finding on an abdominal radiograph or CT and are found in many children with acute appendicitis. Patients who have a retrocecal appendix may have an increase in incidence. Mineral deposits and hard thick stool and constipation combine to produce the appendicolith. Appendiceal calculi, Appendiceal enterolith, or Appendicular lithiasis is the other name for it. Young people and pediatric groups frequently have appendicoliths
MUCOCELE OF APPENDIX – It is an obstructive dilatation of the appendix caused by intraluminal accumulation of mucoid material. It is a fluid-filled growth that develops on the mucosal membrane of the
appendix. Mucocele of the appendix are caused by excessive mucus production and surgery is necessary to remove the appendix.
STUMP APPENDICITIS – Stump appendicitis is the inflammation of the residual appendiceal tissue after an appendectomy (removal of the appendix). This is due to re-inflammation of the residual part of the appendix due to incomplete appendectomy
APPENDICULAR CANCER(CARCINOMA) – Appendicular carcinoma is a type of cancer that grows from cells that are made up of an appendix. There are two main types of appendiceal cancer; epithelial appendiceal cancer and neuroendocrine appendiceal cancer.
Epithelial appendiceal cancer – grows from cells that make up the lining of the appendix. It may also be called adenocarcinoma. These cells help make a jelly-like substance called mucin.
Neuroendocrine appendiceal cancer –Enterochromaffin cells (ECs) are the source of growth in neuroendocrine tumors of the appendix.ECs produce a substance that aids in digestion and bowel motion, This is the most typical form of appendiceal cancer. They are also called carcinoid tumors.
Directly from the appendix, appendiceal cancer can spread to other areas of the abdomen. Generally when it ruptures. Appendiceal carcinoma can readily spread outside of the abdomen through lymph nodes.
DR.KUMARAGURUBARAN is one of the Best Doctors in treating patients with APPENDICITIS and APPENDIX-related diseases.
Services
- Gerd - Gastroesophagel Reflux Disease
- Hiatus Hernia
- Endoscopy & Colonoscopy
- Cholelithiasis ( Gallbladder Stones)
- Appendicitis
- Jaundice
- Obesity
- Liver Cirrhosis
- Pancreatitis
- Inguinal Hernia
- Umbilical Hernia
- Ventral Hernia / Incisional Hernia
- Anal Fissure
- Anal Fistula / Fistula In ANO
- Hemorrhoids Or Piles
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Rectal Prolapse
- Gist's - Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease - IBD -Ulcerative Colitis- Crohns's Disease
- Bowel Perforation - Intestinal Perforation
- Bowel Obstruction - Intestinal Obstruction
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Liver Disorders
- Liver Cancer Hepatoma
- Gastric Disorders
- Stomach Cancer
- Small Bowel Disorders -Small Bowel Intestine Disorders Intra Abdominal Adhsesions
- Small Bowel Cancer ( Small Intestine Cancer)
- Large Intestine- Colon Disorders
- Colon Cancer
- Rectal Cancer
- Meckel's Diverticulum
- Spleen
